[ad_1]
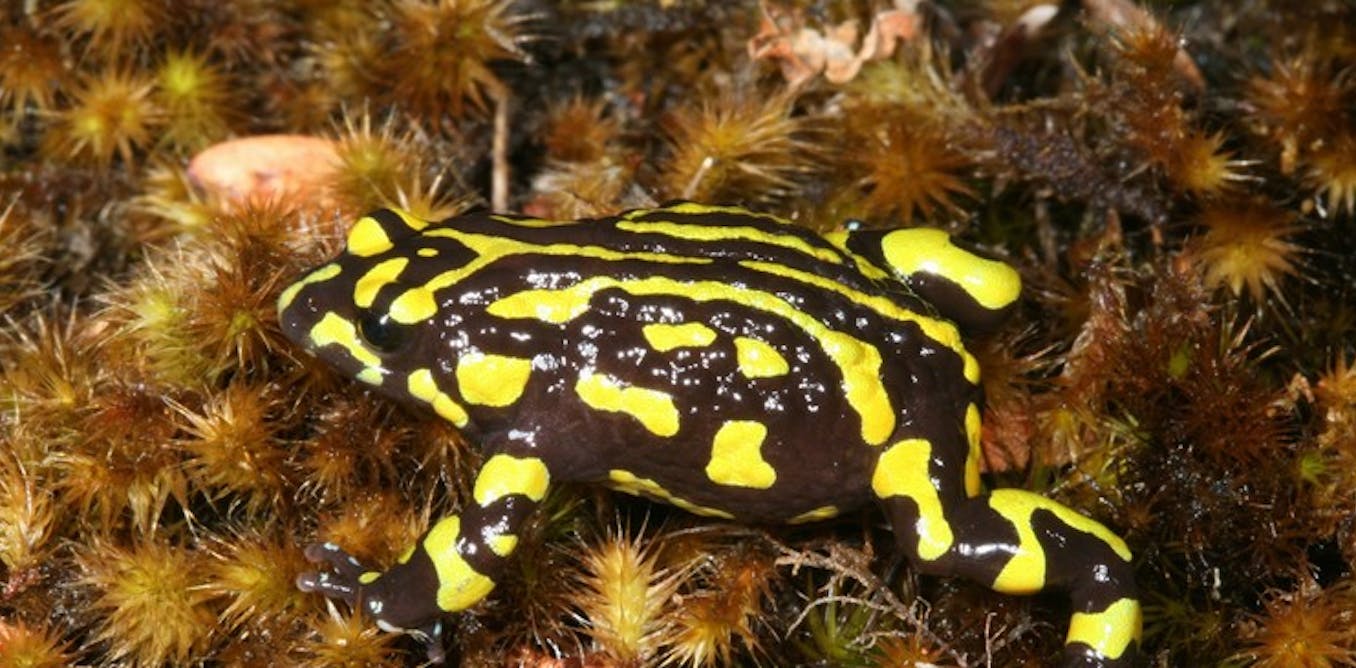
Throughout the late Nineteen Seventies in southeast Queensland, a silent killer arrived on Australian shores. The victims had been our distinctive frogs, with the first to fall being the distinctive gastric brooding frog, closing seen in 1981.
Better than three a very long time on, everyone knows that the killer was a sickness known as chytridiomycosis, attributable to amphibian chytrid fungus.
This fungus is answerable for the presumed extinction of an additional 5 Queensland frog species, and the decline and disappearances of many native populations all through Australia’s complete east coast and tablelands, along with species that had been as quickly as widespread and customary. Globally, a complete lot of amphibian species have moreover suffered most important declines or in the intervening time are considered to be extinct on account of this sickness.
Image Lee Berger
In a study printed in Wildlife Evaluation, we and our colleagues decide seven further Australian frogs which might be at speedy risk of extinction by the arms of chytrid fungus, along with the long-lasting Corroboree frogs (every southern and northern species), Baw Baw frog, observed tree frog, Kroombit tinker frog, armoured mist frog and the Tasmanian tree frog. We predict that the next few years might current the ultimate chance to save lots of plenty of these species.
Whereas the six already extinct Queensland species all declined shortly after the arrival of chytrid, declines in southern areas have been slower. Chytrid is however to achieve in areas of Tasmania’s Wilderness World Heritage House, although the implications usually tend to be merely as excessive.
Our work aimed to prioritise frog conservation efforts all through Australia, determining the species most liable to chytrid, and subsequently most in need of urgent movement. Worryingly, we found that 5 of the seven high-risk species that we acknowledged lack a sustained and adequately funded monitoring program to protect them.
Together with the seven species at speedy risk of extinction, we acknowledged an additional 22 which might be at common to low risk. We moreover assessed the adequacy of current conservation efforts for all of these species, and situated that the majority restoration efforts depend upon the goodwill of individuals and are poorly resourced.
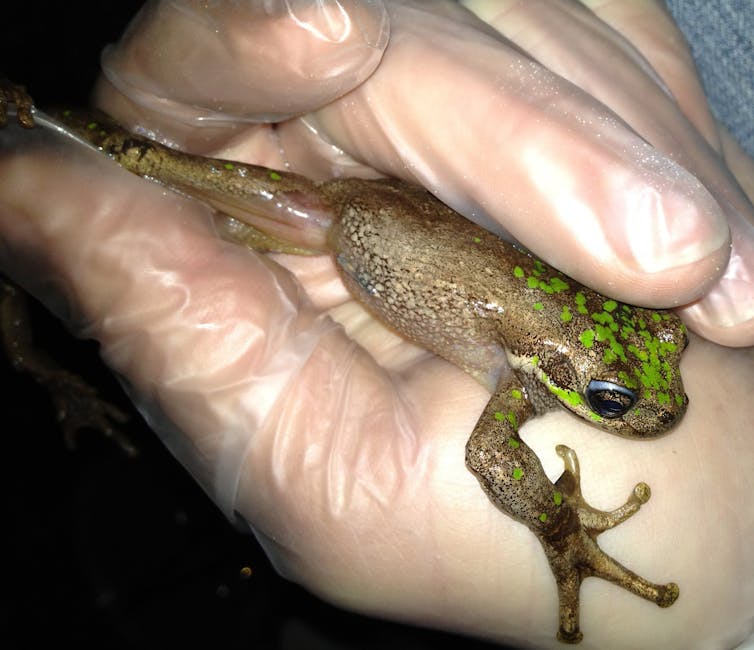

A healthful Tasmanian tree frog.
It is doable to deal with the menace posed by chytrid fungus, nonetheless quick movement is urgently needed. We now have acknowledged six very important administration actions which might be required to forestall extra extinctions of Australian frogs and identify for an neutral administration and evaluation fund to take care of the approaching menace.
The seven species at extreme risk require proactive restoration functions. Essential administration actions might embrace: broad-scale surveys; intensive monitoring; actual risk analysis; the occasion of husbandry methods for the establishment of assurance colonies; re-introductions and or translocations; and new administration strategies to maintain up wild populations.
Australia initially led the world in efforts to find out and deal with chytrid fungus, which was listed as a “key threatening course of” by state and federal governments in 2002
In 2006, a plan was drawn up to struggle the sickness, delivering further evaluation funding and resulting in drastically improved biosecurity measures and elevated understanding of the fungus.
In 2012 the plan was reviewed, and a revised plan that features present evaluation developments now awaits approval. Nevertheless movement is required to deal with the impression of the fungus, and disappointingly there was no funding allotted to implement the model new plan.
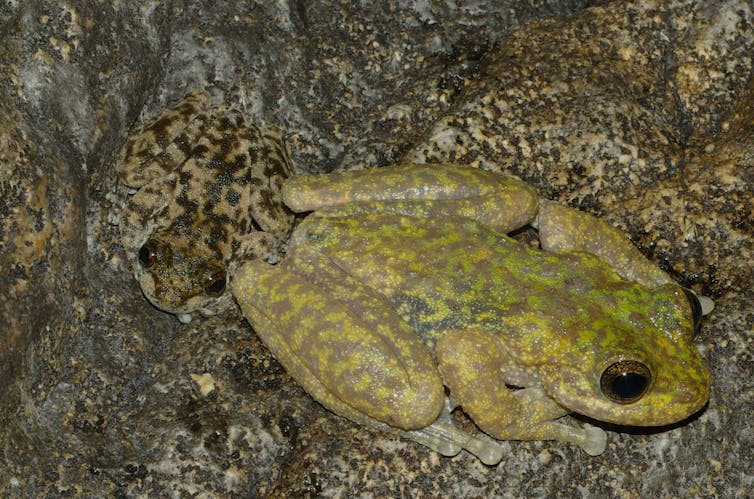

Blink and in addition you’ll miss them: the armoured mist frog (left) and waterfall frog.
The earlier decade has moreover seen most important cuts in every state and federal authorities property for wildlife conservation. State firms have disbanded devoted restoration teams and there was a shift away from single species conservation measures in an effort to maximise restricted funding. That’s whatever the obligations set out in legal guidelines to protect explicit particular person threatened species. These cuts have severely undermined frog conservation efforts.
These frogs should not be allowed to go the an identical method as a result of the Christmas Island pipistrelle, which could arguably have been saved if the federal authorities had heeded scientists’ warnings.
On a constructive observe, administration interventions have saved the critically endangered Southern Corroboree Frog from extinction for now, nonetheless it stays threatened by chytrid fungus and requires ongoing administration and evaluation. With out swift movement, authorities assist and the devoted efforts of many individuals, this species would undoubtedly already be gone.
[ad_2]
